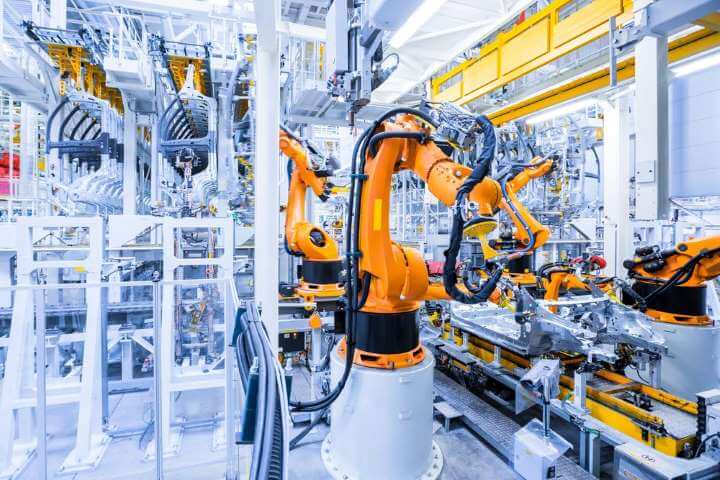
Automation and robots are two distinct technologies, but the terms are often used interchangeably. Together, they have transformed the manufacturing space.
Formerly time-consuming duties are now fully automated with minimal operator input, and robots are taking over more labor-intensive and hazardous tasks from humans.
So how are automation and robotics different, and how are they related?
What Are Robotics and Automation?
Automation is a process that uses software, machines, or other technology to carry out tasks in place of human workers.
Automation is applied to both virtual tasks and physical ones. This methodology can be used for many simple functions, such as a programmable thermostat. It can also perform extremely complex processes (such as in manufacturing) and is sometimes powered by artificial intelligence or machine learning.
Robotics is a field that combines engineering and computer science to design and build robots to perform tasks.
Robots can be separated into three (broad) categories:
- Those that rely entirely on human input to operate
- Semi-autonomous robots that can perform some tasks on their own but require some human intervention/observation
- And Autonomous robots that have the intelligence to perform tasks entirely on their own and can respond to real-world environments with minimal human intervention
Industrial robotics and software for machines allow manufacturers to operate a high-volume production line while improving efficiency and reducing costs. In harsh conditions, they can reduce risks for human workers.
Before you can take advantage of their applications, it’s crucial to understand the distinctions and learn how they can work together to benefit your company.
What Are Automation and Robotics: Types and Scope
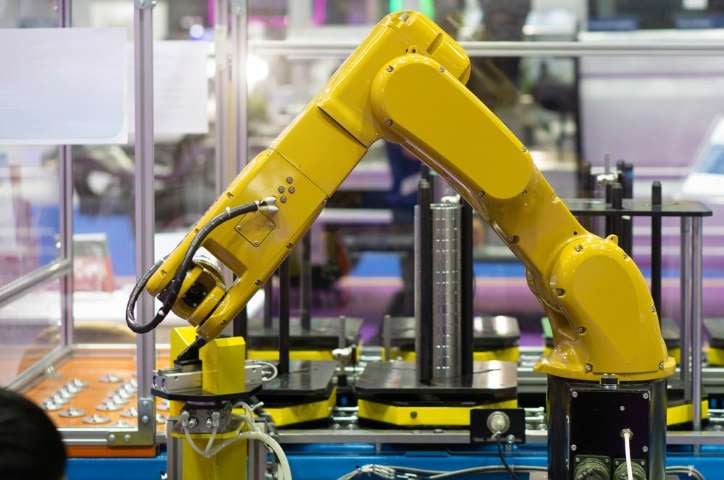

There are three distinct types of automation.
- Software automation uses a computer program to carry out repetitive tasks in a virtual environment. Despite the name, these “bots” are not physical robots, and they can be used to automate tasks such as auto-filling forms or financial services.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) is a type of software automation designed to use a computer’s user interface the same way a human worker would. Some RPA tools are enhanced with machine learning or AI to help them perform rule-based tasks more efficiently.
- Industrial automation uses machines to control physical processes. Common examples include CNC machines and automated inspection equipment. Industrial automation may also include robot automation.
However, not all robots rely on automation technology.
Robotics involves any number of programmable machines that carry out processes. Robots interact with the physical world using sensory input to carry out their tasks. They offer more flexibility than single-function machines because they are reprogrammable. Robots are commonly used for:
- Lifting & Material Handling
- Welding
- Assembling
- Picking & Placing
- Loading & Unloading
Differences Between Automation and Robotics
With the right control systems and automation software, robots can perform complex tasks and operate 24/7 with greater efficiency than their human counterparts. In fact, studies have shown manufacturers can reduce overtime spending and errors by 15% and 25%, respectively, when they integrate robotic technology.
Moreover, robots can handle parts too small for human fingers and with greater accuracy. They are able to achieve a variety of tasks rather than specializing in one task, unlike a traditional assembly worker.
On the other hand, software automation such as implemented RPA can improve employee workflows and allow them to focus on high-value tasks. It can streamline various business tasks through help desk support with chatbots, efficient meeting scheduling, or offering analytics on employee performance.
The benefits of RPA include:
- Free up employee time - RPA bots take over tedious work so your staff can focus their energy elsewhere.
- Reduced costs- RPA can perform repetitive tasks continuously so you can save money on your workforce.
- Easily trackable - It’s much simpler to set up analytics for your bots than it is for human users.
- Improved Governance - Bots are programmed to follow strict protocols, and you program them to flag activity that falls outside the scope of your compliance.
- Easily Scaled - Bots are easily duplicated and reprogrammed for other purposes.
- Better Security - Bots avoid many of the security issues human users create.
However, software automation has limited uses when it comes to performing multiple tasks using one system. You’ll need to create new software solutions for each task you want to automate.
Industrial automation faces similar limitations. While it is excellent at performing repetitive tasks with few variables, machines generally serve one primary purpose. Creating machinery that can perform multiple purposes is what robotics and automation can do when they work together.
More Information On Automation in Manufacturing
How Automation and Robotics Overlap
Automation allows for the creation of collaborative robots that can take instruction from humans. Automation and robots can work hand-in-hand to automate industrial tasks. Together, they offer improved output and efficiency and let you free up your workforce so they can maximize their skills in other areas. Still, there are a variety of issues that can slow things down.
One major factor for any business - small, medium-sized, or large - is the upfront cost. With good planning and efficient implementation, you can achieve a return on investment within two years.
Unfortunately, the process of automation in robotics is often disjointed. It is difficult to connect multiple systems without the right programming software.
Many unexpected costs in implementation arise during the development phase. If you’re stuck in the design process for months building multiple prototypes to work out performance issues, the cost of your project may outweigh the benefits.
Overcoming these hurdles to create customized industrial automation solutions requires sophisticated software for robotics. This enables your engineers and designers to collaborate on projects at peak efficiency. You can also create and test digital models before you invest in physical prototypes.
Is Your SDK Helping, or Holding Your Project Back?
Learn the 3 common pitfalls when selecting a software development toolkit.
Read Case StudyHow to Improve Collaboration Between Robotics and Automation (and Reduce Time-to-Market)
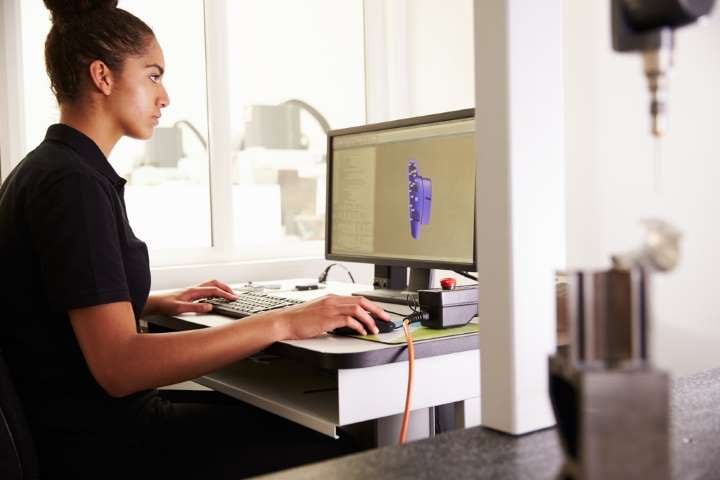

Spatial offers over 35 years of experience developing software development kits (SDKs). We can provide manufacturers with a proven foundation for specialized application development to optimize their workflows, shorten the learning curve, and increase their productivity.
Our software components will allow you to create 3D visualizations of robotic work cells and update tool paths associated with CAD models. Cloud-based CAD collaborations eliminate employee headaches when working with incomplete updates and streamlines communication between teams.
With 3D InterOp, you can import large CAD assemblies easily. Your team can find and isolate specific parts of the models to edit for design iterations. Our integrated design management tools and pre-configured workflows allow your CAD and CAM engineers to extract and duplicate features across version updates quickly.
Spatial’s robotics 3D software toolkits allow manufacturers to maintain focus on the core capabilities rather than starting from scratch. Our simulation application SDKs can reduce data preparation times while enhancing the accuracy of your simulations, so you can reduce your development time and implement your design with confidence.
Contact Spatial today and learn more about how our software solutions can help take your company into the future!