'Form' in mathematics manifests itself in all manners of perspective and discussion. From your earliest mathematics courses, professors drilled home the discipline; “return all answers in simplest form”. My youthful efforts to dismiss the need yielded discussions as such; “OK, please graph this
equation: ![]() " . In a quick second I would naively suggest that at x = -1 the equation is undefined and then I would start plotting points. But alas, this is why form is important.
" . In a quick second I would naively suggest that at x = -1 the equation is undefined and then I would start plotting points. But alas, this is why form is important. ![]() gets factored to
gets factored to 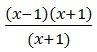 which is simplified to
which is simplified to 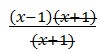 to x - 1, whenever x isn’t -1. Wait, that’s a line. My eighth grade algebra teacher, Mr. Sower, was right, simplest form is important.
to x - 1, whenever x isn’t -1. Wait, that’s a line. My eighth grade algebra teacher, Mr. Sower, was right, simplest form is important.
As you advanced in your course work, you start to define forms of equations by their mathematical representation and to understand advantages and disadvantages of each. Farin, in his book, Practical Linear Algebra, does a nice job outlining the three main forms of an equation of a line and advantages of each in computer graphics:
- Explicit Form: y = mx + b This is the form in every basic algebra book. It’s very conceptual; the coefficients have clear geometric meaning. In computer graphics it’s the preferred form for Bresenham’s line drawing algorithm and scan line fill algorithms.
- Implicit Form:
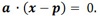 (Given a point p and a vector a that is perpendicular to the line.) The implicit form is very useful for determining if an arbitrary point is on a line.
(Given a point p and a vector a that is perpendicular to the line.) The implicit form is very useful for determining if an arbitrary point is on a line. - Parametric Form:
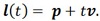 . The scalar value t is a parameter. In this form, we can easily calculate points along the line by use of the parameter, t.
. The scalar value t is a parameter. In this form, we can easily calculate points along the line by use of the parameter, t.
I’m not certain when I internalized that inherent in mathematics is the art, strategy and beauty of 'form'. (I’m a slow learner, it wasn’t Mr. Sower’s fault.) But as my career developed into the commercial implementation of B-rep modeling kernels their translation technologies, 'form' again, became a principal view.
So, for the purpose of this discussion we define 'form' of geometric curves and surfaces in three ways: analytic, B-spline and procedural representations. All three of the major solid modeling kernels, ACIS, CGM, and Parasolid, maintain their geometry in either of these three forms, or sometimes as dual representations. [1]
- Analytic: geometry which can be represented explicitly by an equation (algebraic formula), for example: planes, spheres, and cylinders. These equations are very light weight and they intrinsically hold characteristics of the surface, for example the centroid of a sphere.
- B-spline: geometry represented by smooth polynomial functions (in parametric form) that are piece-wise defined. Generally used to represent free-form surfaces. Advantages of B-splines are their ability to represent many types of geometry and bounding boxes are easy to calculate.
- Procedural: geometry represented as an implicit equation or algorithm. For example, the IGES specification has tabulated cylinders and offset surfaces as defined procedural surfaces. The advantages are precision and the knowledge of progenitor data to understand design intent.
From this perspective, each of the major kernels has thought long and hard about the best form for each geometry type. In some cases it’s self-evident and easy. If you are modeling a sphere, the analytic form is clearly best. It’s a lighter weight representation and the full extents of the surface are defined. Even more, imagine doing a calculation requiring the distance between a point and a sphere. In this “special” case, you simply compute the distance between the point and the centroid of the sphere, subtract the radius and you’re done. If the sphere was in the form of a b-spline it’s much more computationally expensive. Despite this translation solutions still don’t get this preferred form right. Now imagine you’re a CMM application and you purchased the solution that translates spheres to B-splines? Your app is horribly slow.
Although spheres are a trivial example, more complex geometries become intriguing. In what form should you prefer a helical surface? Or an offset surface? ACIS has preferred multiple versions of helical surfaces over the years. Early on the preferred version was a procedural sweep surface with either a procedural rail curve or a b-spline rail curve. (The rail curve is what defines the helical nature of the surface). If the surface was translated in from Parasolid it came in as a generic b-spline surface. But the need to understand different characteristics of the helical surface soon became apparent. For example, the hidden line removal algorithm and intersectors all needed to understand the pitch and handedness to efficiently work with the geometry. To that end, ACIS moved to a procedural surface definition with an analytical representation of the helical rail curve.
The offset surface is an excellent example where the CGM developers and the ACIS developers came to different conclusions. In ACIS the offset surface is procedural; evaluate the progenitor and shoot up the surface normal the offset distance. ACIS choose this representation for preciseness and compactness of data. In addition, in ACIS, if you offset an offset surface the progenitor of the original offset becomes the progenitor for the second or third or fourth offset and more geometry sharing is possible. But all of this comes at a cost. Procedural surfaces, although exact, may have a performance penalty and may introduce unwanted discontinuities. The CGM developers decided the best strategy here was to create b-splines for offsets.
So what does this all have to do with translation? The key point here is; you need to understand what the preferred forms are for each of the modeling kernels. In each of these systems you can easily slip in geometry in non-optimal forms causing immense grief when doing downstream modeling operations. I spoke earlier about the translator solution that goofed up even a simple conversion of spheres. And the CMM application that purchased that translation solution? In short, don’t let that be you.
[1] For this discussion I’m going to leave off polyhedral form.



.jpg?width=450&name=Application%20Lifecycle%20Management%20(1).jpg)














