Table of Contents |
Before we look at how digital twins are transforming manufacturing, we need to understand where manufacturing stands right now.
A World Still Driven by Traditional Manufacturing
Despite living in an increasingly digitized real world, traditional manufacturing remains vital to our economy. According to a 2021 study conducted by the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM), manufacturing accounts for an annual 10.94% of U.S. economic output and employs over 12 million people.
For a long time, however, manufacturing has been held back by certain unassailable limitations: Whether it’s the continuous upkeep of expensive machinery or adherence to an evolving roster of regulatory compliance guidelines, optimizing factory performance has become a major challenge.
But all that is rapidly changing with the advent of a technology known as intelligent digital twins (or, simply, “digital twins”). In this article, we unpack how digital twins are transforming manufacturing and why implementing this technology is integral to your organization’s future.
Digital Twins have Transformed Architecture, Engineering, and Construction
Find out how BIM gives designers, builders, and property managers oversight of their building
Learn More
What Is a Digital Twin?
A digital twin is defined as an exact virtual doppelgänger of a physical object, process, or environment. In other words, it’s a sophisticated software model that acts as a digital re-creation of a material counterpart.
The concept of digital twins was was introduced in 1992 and was popularized in manufacturing a few years later. But it wasn’t until 2010 that NASA became the first organization to successfully adopt the technology in an effort to refine spacecraft modeling.
Since then, the number of real-world applications for digital twins has swelled tremendously.
The ability to create a digital version of a physical object that not only looks the same but acts the same has proved indispensable. Sophisticated algorithms can reliably detect anomalies, anticipate repairs, optimize usage and lifespan, and simulate performance.
As a result, digital twins have made it possible to overcome the ceiling effect that has plagued manufacturers for decades. This virtual 3-D replica, which can be accessed with a VR headset or desktop, is a promising solution for reducing downtime and improving factory efficiency.
How Digital Twins Work
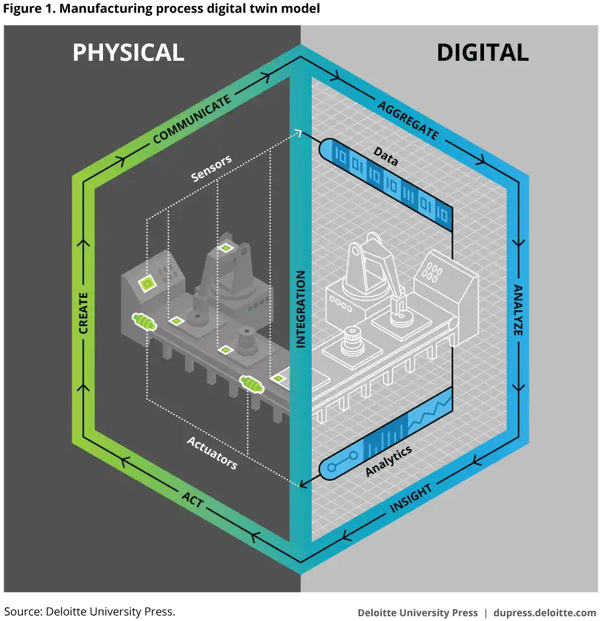
Source: Deloitte
Technical details aside, setting up digital twins is fairly straightforward.
This first step is world-building. In manufacturing, for example, blueprint data about a physical factory and its equipment is fed into a 3D mapping program to produce a precise virtual environment. Next, real-time monitors and sensors are used to extract dynamic performance data from machinery.
With the working model complete, it’s time to leverage the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Advanced algorithms establish an operational baseline by “observing” the digital twin and “learning” to distinguish between normal and anomalous performance behavior.
Traditionally, most monitoring systems would only provide information about each piece of equipment in isolation. In the absence of a holistic approach, it quickly became confusing to manage and easy to overlook important cues.
Digital twins, however, aggregate machine data within its environmental context and in relation to other machines. This produces a consolidated, cohesive, and comprehensive picture of your operations at large, making it possible to derive actionable insight.
How Digital Twins Are Transforming Manufacturing Today

To fully grasp the concept of digital twins, we need to see it at work. This requires us to take a little trip to the beautiful Bavarian town of Regensburg, Germany. Regensburg is widely considered the best-preserved medieval town in Europe. A lesser-known fact is that Regensburg is also home to not one, but two, enormous BMW production facilities.
The first facility is exactly what you’d expect: a physical plant that cranks out 800 new cars per day. The second facility looks and behaves exactly the same as the first—the only difference is that it exists entirely in the digital ether.
Indeed, the BMW factory’s digital twin emulates every part of the production process: avatars of workers carrying equipment down the production lines, technicians shaping the metal frame of each vehicle, and quality control specialists examining every component in minute detail.
The digital replica, accessed by screen or virtual reality (VR) headset and considered a virtual one in real life, has been a crucial tool in reducing waste, designing complex technical plans, upgrading infrastructure, and fighting climate change. But auto manufacturing isn’t the only sector singing the praises of digital twin technology.

In healthcare, digital twins are used to create precise reproductions of internal organs that are otherwise difficult to study in real life. Meanwhile, in the aerospace industry, defense contractors have leveraged digital manufacturing capabilities to design and prototype next-gen fighter jets for the U.S. Air Force.
There is no shortage of real-life examples. It’s clear how twins are transforming manufacturing more than any other piece of technology since the First Industrial Revolution replaced manpower with steam.
Why Digital Twins Are Essential to Manufacturing
Maintaining costly machinery requires a lot of care and attention. This can be especially difficult in the face of ever-changing work conditions and tight delivery deadlines. Despite the aid of software solutions, many manufacturers have come up against an impenetrable optimization ceiling—both in terms of productivity and production times.
But digital twins are changing the game by helping manufacturers optimize efficiency, value, and innovation at every level. This is achieved by providing real-time insight into the complete operational state of a factory based on its many elements and dynamics. The result is:
- Reduced downtime
- Increased safety
- Increased throughput
- Predictive maintenance
- Decreased emissions
- Shortened delivery cycles
- Decreased production costs
- Increased product quality
It’s no surprise that digital twins have grown increasingly ubiquitous in the manufacturing industry. This is particularly true of organizations dealing with expensive physical components in short supply, such as the aerospace, healthcare, auto, urban planning, and construction industries.
Don’t Make the Same Mistake
When users have dozens of software suite choices, what makes the difference for your users is interoperability
Learn More
Industry 4.0 and the Future of Digital Twins
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) promises a radical transformation in manufacturing. Intelligent automation has already united a wide array of cutting-edge technologies that are ushering in the next paradigm shift, including:
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Machine learning (ML)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Cyber-physical systems (CPS)
- Cloud computing
- Cognitive computing (CC)
Digital twins leverage many of these to deliver true interconnectedness and decentralized decision-making. And there is no doubt that this trend is here to stay. The global digital twins market was valued at $3.1 billion in 2020. By 2026, that valuation is expected to exceed $48.2 billion.
By harvesting data in real-time frames from physical objects and processes within the factory, continuous productivity improvements are achieved. This ensures a steady stream of actionable insight is always ready to be derived.
Learn More
Get the Big Picture of Your Manufacturing Operations, With Spatial
As we’ve seen, digital twins improve operational efficiency in a variety of novel ways. From design and engineering to assembly and service, this highly scalable technology has enabled manufacturers to integrate their operations into a seamlessly interconnected digital network.
Are you ready to optimize productivity, reduce production times, and improve equipment life cycles? At Spatial, we can guide you through a complete digital transformation to achieve a competitive edge in your industry. Contact us today to discover how.
Improve Functionality While Reducing Time to Market…Really?Spatial’s SDKs help businesses like yours improve user experience, prolong the application’s market presence, and boost profitability. Find out how we can help you supercharge your next application. |
Integrate Next-Gen Technologies With Spatial’s SDKs |