Additive manufacturing (3D Printing) is sweeping across the industrial automation world.
Instead of creating molds and removing material, manufacturers can now simply add layers of material to produce items at a lower cost and with less waste. Metal additive manufacturing (Metal 3D Printing) in particular is gaining traction and becoming especially popular in industries like aerospace.
According to a recent AMPOWER report, the metal additive manufacturing market is expected to grow by 27.9% by 2024. With metal additive manufacturing, companies can construct a strong, highly intricate metal part with fewer materials and less effort than traditional manufacturing processes.
To keep up with industry trends, here’s your quick guide to metal additive manufacturing.
Metal Additive Manufacturing Explained
Unlike conventional manufacturing that requires molds and trimming, additive manufacturing builds items from the ground up using sophisticated 3D printing equipment. The basic process takes place in five steps:
- Create a digital model.
- Prepare it for printing by hollowing, editing hole sizes, adding supports, etc.
- Slice the 3D model into layers.
- Print the part layer by layer.
- Post-processing into the final product.
While the process remains largely the same, there are multiple ways to print products using metal additive manufacturing. Here are a few of the most common:
- Powder bed fusion – Metal powder is placed on the manufacturing table, and high-energy electron lasers precisely fuse the powder layer by layer to create the final product.
- Metal jetting – The metal material is melted and applied directly to the manufacturing table. The liquid metal quickly cools, and new layers get added until the final product is finished.
- Furnace-infused alloy – Metal powder is joined with a liquid binding agent. As more layers of the binding agent get added, the final product takes shape.
Each type of metal additive manufacturing can create multiple parts with a wide variety of materials. Some of the most popular metal additive materials used in additive manufacturing are nickel alloys such as Inconel 718 and Inconel 625, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
Pros and Cons of Metal Additive Manufacturing (Metal 3D Printing)

There are many benefits of metal additive manufacturing, but it’s not ideal for every type of manufacturing. Here is a quick guide to metal additive advantages and disadvantages of using an additive manufacturing system for building metal products.
Advantages
- Reduce space and cost requirements for storing parts by giving you the ability to produce parts on-demand locally.
- Less waste without the need to trim or cut parts from larger materials, which also helps to reduce manufacturing costs.
- Quickly produce new products without needing to create molds.
- Faster prototyping can quickly accelerate product development and can help you gain a competitive edge.
- No assembly required. Additive manufactured parts can be printed in their entirety without needing to put multiple parts together.
- Construct highly intricate parts with minimal effort or skill.
Disadvantages
- Slow build times mean additive manufacturing isn’t ideal for large production runs.
- Higher upfront costs with more expensive equipment needs.
- Product size is limited to the constraints of the additive manufacturing system. Consumer-grade printers, for example, typically have print beds that are smaller than one cubic foot.
|
Want to learn more about additive manufacturing? Check out these blogs from Spatial: |
Applications of Metal Additive Manufacturing
Originally, metal additive manufacturing was used mainly for prototyping. Manufacturers could quickly design and print test-ready products before investing in molds and equipment for larger production runs using metal additive software. As the technology advanced and additive manufacturing became more affordable, it has been adopted by a wide variety of industries.
The aerospace industry has been one of the major adopters of additive manufacturing. Aerospace companies are using Additive Manufacturing (“AM”) to design and construct highly intricate metal parts that otherwise would not have been possible using conventional methods.
Since there’s less waste, aerospace manufacturers can cut down on weight without sacrificing structural integrity, which is essential when designing aircraft.
The medical industry has also used additive manufacturing to create unique tools and instruments for specific procedures. Medical professionals no longer have to wait for tools to be designed and built by a manufacturer. They can create the exact tools they need in a fraction of the time - at a much lower cost, in-house to assist with complicated procedures.
Optimize Production with Metal Additive Manufacturing
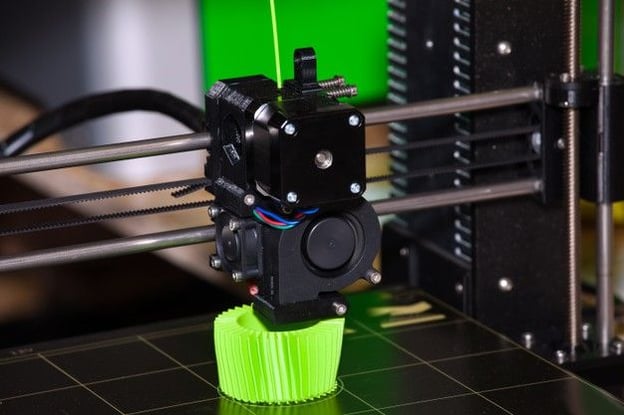
Metal additive manufacturing might not replace conventional manufacturing processes, but it offers many sizable benefits for manufacturers in a wide variety of industries.
If you’re interested in accelerating metal additive manufacturing, talk to the experts at Spatial. For over 35 years, we have helped manufacturing businesses develop 3D software applications to digitize their workflow with our 3D Modeling Software Development Kits and expertise.
Contact us to learn how Spatial can elevate your manufacturing process and digitize your workflow.






.jpg?width=450&name=Application%20Lifecycle%20Management%20(1).jpg)






